Murtala Aminu Bamanga
Introduction
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) have been widely considered as an important technology in the 21st century. It is deployed in tremendous application ranging from monitoring, surveillance, forest fire detection etc.
WSN technology is a promising technology for achieving seamless, energy efficient, reliable and low cost monitoring and control in smart grid. Smart grid is a modern electric power grid infrastructure for improved efficiency reliability, and safety with smooth integration of renewable energy and alternative energy sources, through automation control and modern communication techniques.
WSNs are applied through the entire process of the smart grid i.e. from the generation, transmission and distribution, and the consumer side. Some of the applications include:
- Load management and control
- Wireless automatic meter reading (WAMR)
- Equipment fault diagnostic
- Remote monitoring
- Fault detection
- Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI)
- Residential energy management; amongst others.
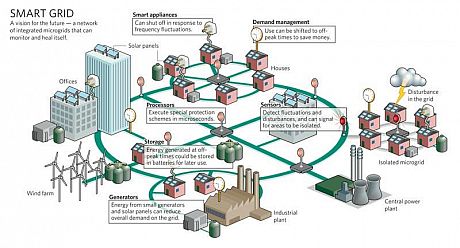
(Image Source: http://horizonenergy.blogspot.co.uk/)
Challenges
Though WSNs brings about a lot of advantages to the smart grid technology, it also brings up a lot of challenges because of the harsh and complex electric-power environment. The traditional protocols (MAC, Routing and Transport) for conventional wireless network need to be modified because of its unique characteristics and constraints in terms of energy efficiency and storage capacity. Real-time communication of WSNs needs to be investigated in order to tackle time sensitive applications in the smart grid. The research will have high impact and also open up new dimensions for future research of WSNs and smart grids.

